Efficiently managing background tasks is an essential aspect of modern application development. Whether it’s processing large datasets, sending emails, or handling delayed notifications, background jobs ensure your application remains responsive and scalable. One of the most robust solutions for managing these tasks in .NET applications is Hangfire. In this complete guide, we will explore everything you need to know about Hangfire, from setup to advanced configurations, ensuring you can make the most of this powerful tool.
What is Hangfire?
Hangfire is an open-source library that enables developers to schedule and manage background jobs in .NET applications. With its seamless integration into the .NET ecosystem, Hangfire eliminates the need to create a separate Windows Service or Cron job scheduler. It supports persistent storage, allowing background tasks to be reliably executed, even after application restarts.
Key Features of Hangfire
- Ease of Use: A simple API that allows developers to create and manage background jobs effortlessly.
- Reliable Storage: Supports SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Redis, and more for persistent job storage.
- Built-in Dashboard: A web-based monitoring tool to track job execution, retry attempts, and performance.
- Job Types: Supports various job types such as Fire-and-Forget, Delayed, Recurring, and Continuations.
- Scalability: Works seamlessly in distributed environments, scaling across multiple servers.
Getting Started with Hangfire: Installation and Setup
To begin using Hangfire, follow these steps:
Install the NuGet Package First, run the following command in your package manager console:
Install-Package HangfireAdd Hangfire to Your Application Next, open the
Startup.csfile and configure Hangfire within theConfigureServicesmethod:csharppublic void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddHangfire(config => config.UseSqlServerStorage("YourConnectionString"));
services.AddHangfireServer();
}Enable the Dashboard Finally, to enable the Hangfire Dashboard, add it in the
Configuremethod:public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
app.UseHangfireDashboard();
app.UseHangfireServer();}
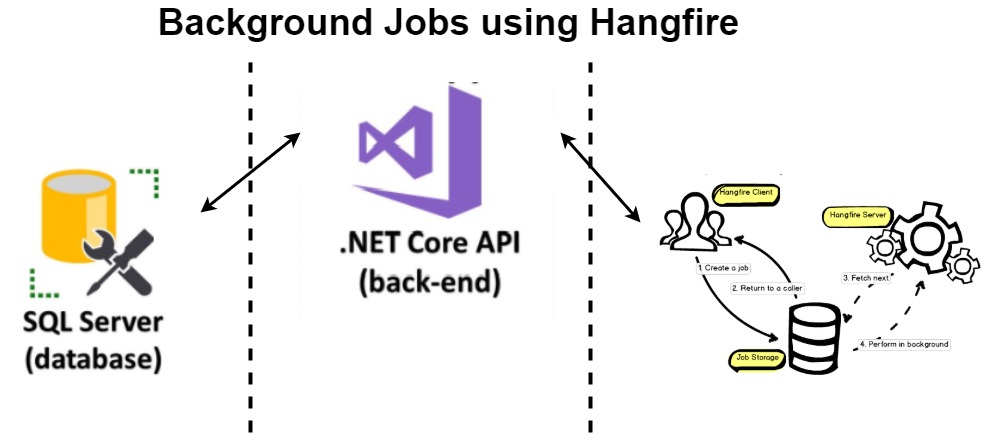
Job Storage Configuration
Hangfire requires a persistent storage mechanism to store job data. Common options include:
- SQL Server
Use theUseSqlServerStoragemethod with your connection string. - Redis
Install the Redis storage provider package and useUseRedisStorage.
Types of Jobs in Hangfire
Hangfire supports multiple job types, each catering to specific use cases:
1. Fire-and-Forget Jobs
These jobs execute immediately after being created. They are ideal for tasks like sending BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Fire-and-Forget Job Executed"));
2. Delayed Jobs
Execute a job after a specified time delay.
BackgroundJob.Schedule(() => Console.WriteLine("Delayed Job Executed"), TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5));
3. Recurring Jobs
Run jobs on a schedule, similar to Cron jobs.
RecurringJob.AddOrUpdate("my-recurring-job",
() => Console.WriteLine("Recurring Job Executed"), Cron.Daily);
4. Continuation Jobs
Run a job after the successful execution of another job.
var jobId = BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Initial Job Executed"));
BackgroundJob.ContinueWith(jobId, () => Console.WriteLine("Continuation Job Executed"));
Advanced Hangfire Features
Error Handling and Retries
Hangfire automatically retries failed jobs. By default, it retries a job 10 times before marking it as failed. You can customize this behavior globally or for individual jobs.
GlobalJobFilters.Filters.Add(new AutomaticRetryAttribute { Attempts = 5 });Job Prioritization
Hangfire allows you to define queues to prioritize jobs. For instance, you can set up “critical” and “default” queues:
BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Default Queue Job"));
BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Critical Queue Job"), "critical");
Performance Monitoring
The built-in dashboard provides detailed insights into job processing, including success rates, failures, and execution times. Access the dashboard at /hangfire.
Using Hangfire in Distributed Systems
Hangfire supports distributed job processing, allowing multiple servers to process jobs simultaneously. This is crucial for scaling applications. Simply configure the same job storage across all servers.
Best Practices for Using Hangfire
Securing the Dashboard
To safeguard your Hangfire Dashboard, implement authentication, ensuring only authorized users can access it.app.UseHangfireDashboard("/hangfire", new DashboardOptions { Authorization = new[] { new MyAuthorizationFilter() } });Monitoring Job Performance
Keep an eye on job performance via the dashboard to pinpoint any potential performance bottlenecks, allowing you to optimize job execution as needed.Using Dependency Injection
Utilize Dependency Injection (DI) to pass services into your Hangfire jobs for better code organization and testability.public class MyJob { private readonly IMyService _service; public MyJob(IMyService service) { _service = service; } public void Execute() { _service.DoWork(); } }\Managing Long-Running Tasks
For tasks that take longer to complete, set appropriate timeouts and monitor system resources to avoid overloading the system.Utilizing Custom Queues
Implement custom queues to prioritize critical jobs and ensure they are processed before less important tasks.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Job Overlap
To prevent multiple instances of the same job from running simultaneously, use mutex locks or assign unique identifiers to each job.Failed Jobs
Regularly check for jobs that have failed, and set up alert notifications for high-priority failures so you can address issues quickly.Storage Optimization
Periodically clean up completed jobs to avoid unnecessary storage consumption and ensure optimal performance.var manager = new RecurringJobManager(); manager.RemoveIfExists("my-recurring-job");
Conclusion
Hangfire is an excellent tool for handling background tasks in .NET applications, offering reliable, scalable job management. With features like recurring jobs, delayed tasks, and a comprehensive monitoring dashboard, it’s an essential framework for developers. By following these best practices, you can enhance the efficiency of your applications and get the most out of Hangfire.

🏆 Upwork Top Rated Professional ⭐ 5-Star Ratings
🔰10+ years of experience
⌚ Full-Time Availability
ASP.NET CORE | REACT | ANGULAR | NODE JS | WEB API | C# | MVC | SQL | PHP | MICROSERVICES | DOCKER | SQL SERVER | NoSQL | Blazor | CLOUD | AWS | Azure | Astro | VUE